Understanding Technical Analysis
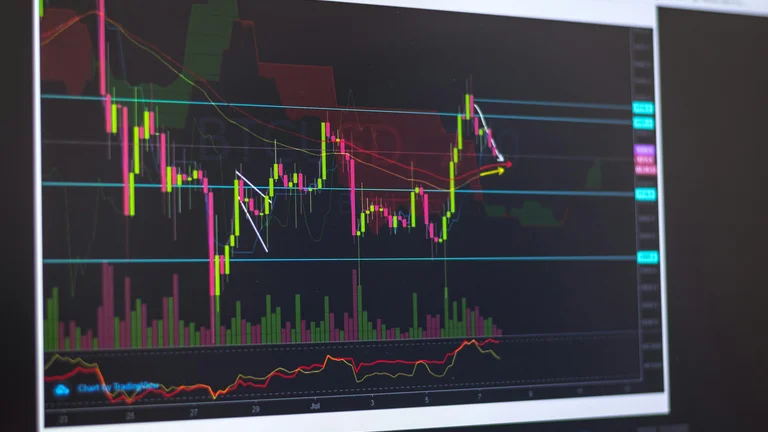
Technical analysis focuses on price movements and trading volumes to predict future market behavior. Investors look for patterns and indicators that help assess the strength or weakness of a security. Unlike fundamental analysis, which studies a company's financial health, technical analysis aims to identify market trends through charts and historical data.
Traders often utilize various tools to analyze trends. Common tools include moving averages, Bollinger Bands, and the Relative Strength Index (RSI). Each of these tools interprets price data differently, providing unique insights into market conditions. This analysis can guide investors in making informed decisions on buying or selling assets.
Key Components of Technical Analysis
Two fundamental components underpin technical analysis: price charts and technical indicators. Price charts graphically represent asset prices over specific periods. Investors typically utilize line charts, bar charts, and candlestick charts. Each chart type offers different insights into price trends and market behavior.
Technical indicators serve as mathematical calculations based on price and volume. Indicators help identify trends and point out potential reversal points. For instance, the Moving Average convergence divergence (MACD) is a widely-used indicator that helps investors gauge momentum and trend direction.
Patterns and Signals
Technical analysis often revolves around the recognition of patterns and signals. Patterns like head and shoulders, double tops, and triangles hint at potential price direction changes. Identifying these patterns helps investors predict future price movements, increasing their chances of making profitable trades.
Additionally, signals generated from indicators provide entry and exit points in the trading strategy. For example, when the MACD crosses above the signal line, it can indicate a potential buying opportunity. Conversely, a cross below may suggest it's time to sell.
Timeframes in Technical Analysis
Investors use various timeframes in technical analysis, including minutes, hours, days, weeks, and even months. Each timeframe carries its significance based on the trading style. Day traders often focus on shorter timeframes, like 5-minute or 1-hour charts. Swing traders may prefer daily or weekly charts to capture medium-term trends.
Long-term investors might rely on weekly or monthly charts to evaluate price trends. Different timeframes allow investors to approach the market from various perspectives, adapting their strategies accordingly. Selecting the right timeframe is crucial to aligning analysis with one’s investment goals.
Limitations of Technical Analysis
While valuable, technical analysis is not foolproof. One limitation is that it often relies on past price data, which does not guarantee future performance. Sudden market changes, news events, or economic shifts can quickly overturn market predictions established through technical analysis.
Moreover, technical analysis can become subjective. Different investors may interpret the same chart or indicator differently, leading to varying conclusions. This subjectivity can result in conflicting trading decisions, complicating the analysis process.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Price Charts | Visual representation of asset prices over time. |
| Technical Indicators | Mathematical calculations derived from price and volume trends. |
| Trading Patterns | Recognizable formations that signal potential price movements. |
| Timeframes | Various durations (minutes, days, weeks) to analyze trends. |
| Limitations | Subjectivity and reliance on historical data may affect predictability. |
FAQ - Technical Analysis for Investors
What is technical analysis?
Technical analysis is a method used to predict future price movements of assets based on historical price data, trading volumes, and market trends.
How do I get started with technical analysis?
Begin by learning the basics of price charts, common patterns, and technical indicators. Practice analyzing charts to enhance your understanding.
What are some common technical indicators?
Popular indicators include moving averages, RSI (Relative Strength Index), MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence), and Bollinger Bands.
Can technical analysis predict stock prices accurately?
While technical analysis can provide insights and probabilities, it cannot guarantee accuracy due to market unpredictability.
Is technical analysis better than fundamental analysis?
Both analyses serve different purposes; technical analysis focuses on price patterns while fundamental analysis evaluates a company's financial health.
Technical analysis is a predictive tool for investors that examines price movements and volumes to forecast future market behavior. By using charts and indicators, investors can identify trends and potential trading opportunities effectively.
Conclusão sobre Technical Analysis for Investors.